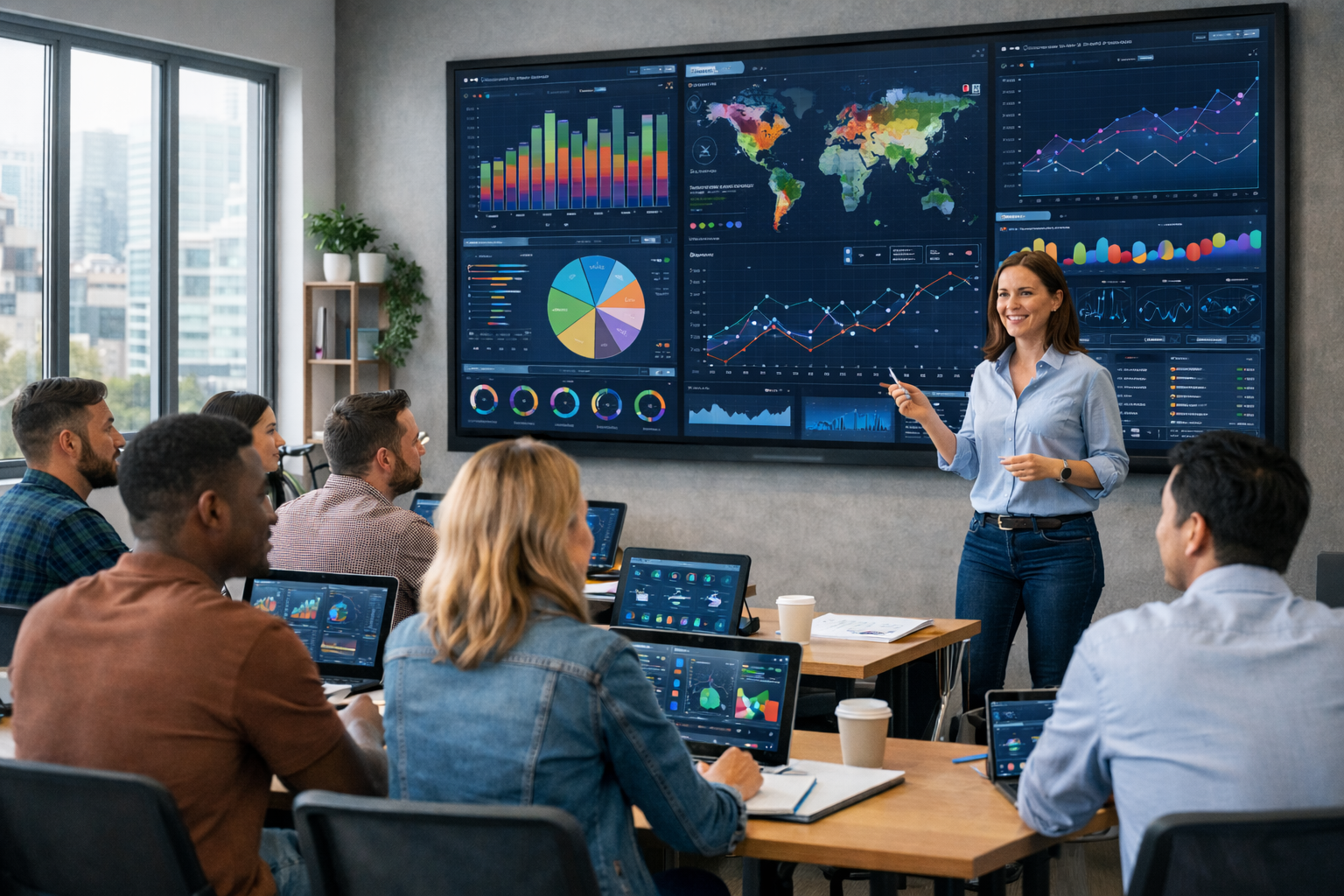
Data & Analytics has become the backbone of modern decision-making. From small businesses to global enterprises, organizations rely on data to guide strategy, measure performance, and predict future outcomes. However, raw data alone does not create insight. The real power comes from data visualization — the process of transforming complex datasets into visual formats that are easier to understand, interpret, and act upon.
This beginner-friendly guide explains what it is, why it matters in data & analytics, the core principles behind it, common chart types, tools, and technical best practices. Whether you are a student, business professional, or aspiring analyst, this article will help you build a solid foundation. If you’re just starting out, reviewing a complete beginner’s guide to data visualization can help reinforce core concepts and chart types before moving to advanced analytics applications.
It is the graphical representation of data using visual elements such as charts, graphs, maps, and dashboards. Instead of reviewing spreadsheets filled with numbers, users can quickly interpret patterns, trends, and relationships through visual formats.
In the field of data & analytics, and serves as the bridge between raw datasets and strategic decision-making. It transforms structured and unstructured data into meaningful visual stories.
For example:
- A sales dataset with 10,000 rows becomes a monthly revenue trend line.
- Website traffic logs become a traffic source pie chart.
- Customer demographics become a heat map or bar chart.
Without It, even accurate data may fail to communicate its insights effectively.
Data visualization plays a critical role in analytics for several reasons:
Large datasets can be overwhelming. It condenses thousands of data points into understandable visuals.
Human brains process visual information faster than text or numbers. Visual analytics makes it easier to detect correlations, seasonal trends, and anomalies.
Business leaders rely on dashboards and reports to make informed decisions. Clear visuals reduce ambiguity and support faster strategic action.
Data visualization enables technical analysts to communicate findings to non-technical stakeholders.
Unexpected spikes, drops, or irregular patterns become immediately visible in charts.
In short, visualization turns data into insight, and insight into action.
Good data visualization is not just about creating charts. It requires design thinking, technical accuracy, and clarity.
The visualization must represent the data truthfully. Avoid manipulating axes or scales in ways that mislead viewers.
Avoid unnecessary colors, effects, or 3D visuals that distract from the data. Simplicity enhances understanding.
Different types of data require different visual formats. Using the wrong chart can distort interpretation.
Always label axes, include units, and provide legends where necessary.
Before creating a chart, ask: What insight am I trying to communicate?
These principles ensure your work aligns with professional standards in data & analytics.
Understanding data types is essential before selecting visualization techniques.
Represents categories or groups (e.g., gender, region, product type).
Includes discrete and continuous values (e.g., revenue, age, temperature).
Data collected over time (e.g., monthly sales, daily website visits).
Location-based data (e.g., sales by region).
Each type influences the choice of visualization.
Beginners in data & analytics should understand the most frequently used charts.
Best for comparing categories.
Example: Comparing product sales across regions.
Ideal for time-series data.
Example: Tracking revenue growth over 12 months.
Shows proportions within a whole.
Best used when categories are limited.
Displays relationships between two numerical variables.
Example: Advertising spend vs. sales revenue.
Shows distribution of numerical data.
Useful for analyzing frequency patterns.
Uses color intensity to represent values in a matrix format.
Common in performance analysis.
Choosing the correct visualization ensures clarity and insight.
While visualization appears simple, it relies on technical concepts in data & analytics.
Before visualization, data must be cleaned:
- Remove duplicates
- Handle missing values
- Standardize formats
- Correct inconsistencies
Data may require aggregation, normalization, or grouping before visualization.
For example:
- Converting daily sales into monthly totals.
- Calculating percentage growth.
Summarizing large datasets improves readability and reduces noise.
Structured data models improve dashboard efficiency and scalability.
Without proper preparation, visualizations can misrepresent information.
Several tools are commonly used in data & analytics.
- Microsoft Excel
- Google Sheets
These are beginner-friendly and suitable for small datasets.
- Tableau
- Power BI
- Looker
These tools support interactive dashboards and large datasets.
- Python (Matplotlib, Seaborn, Plotly)
- R (ggplot2)
These are powerful for advanced analytics and automation.
The choice of tool depends on dataset size, technical skill level, and project complexity.
Modern data & analytics relies heavily on dashboards.
A dashboard combines multiple visual elements into a single interface. It allows users to:
- Monitor KPIs (Key Performance Indicators)
- Filter data dynamically
- Drill down into detailed views
- Compare metrics side-by-side
Interactive visualization enhances exploration. Users can click, filter, and adjust views to uncover deeper insights.
Technical considerations for dashboards include:
- Performance optimization
- Data refresh scheduling
- Responsive design
- User access control
Beginners often encounter several issues.
Too many charts on one page reduce clarity.
For example, using a pie chart for complex comparisons.
Truncated axes can exaggerate differences.
Missing units or unclear legends confuse users.
Color should highlight insight, not distract.
Avoiding these mistakes improves professionalism and readability.
If you are starting in data & analytics, follow these best practices:
- Start with a clear objective.
- Understand your audience.
- Clean your data before visualization.
- Use consistent formatting.
- Limit color usage.
- Test readability on different devices.
- Validate numbers before presenting.
These habits ensure long-term success in analytics projects.
Data visualization is not just technical; it is narrative.
A strong visual story includes:
- Context: What problem are we solving?
- Evidence: What does the data show?
- Insight: What does it mean?
- Action: What should be done?
Storytelling makes analytics persuasive rather than purely informational.
For example:
Instead of showing a declining sales chart alone, explain possible causes and recommend actions.
This approach aligns data & analytics with strategic business impact.
The field continues to evolve.
AI-powered tools now suggest chart types automatically.
Businesses increasingly require live dashboards.
Machine learning enhances insight discovery.
More non-technical users access visualization tools.
As data volumes grow, visualization becomes even more critical.
Data visualization is a fundamental component of data & analytics. It transforms raw data into clear, actionable insights that support smarter decision-making. By understanding core principles, selecting appropriate chart types, applying technical preparation methods, and avoiding common mistakes, beginners can develop strong visualization skills.
Whether you use spreadsheets, business intelligence tools, or programming languages, the goal remains the same: communicate data effectively.
As organizations continue to rely on analytics for growth and innovation, mastering data visualization will remain an essential skill in the digital age.